The news that Disney settles ESPN streaming fees class action lawsuit has caught the attention of millions of streaming subscribers. This high-profile case centers on claims that Disney drove up live TV streaming costs by forcing ESPN into base packages. For years, viewers paid higher bills without the option to skip sports channels.
Now, with the announcement that Disney settles ESPN streaming fees class action lawsuit, consumers are eager to learn if they could receive compensation. The settlement could reshape how streaming services bundle channels. As Disney Settles ESPN Streaming Fees Class Action Lawsuit, the decision may mark a turning point for affordable online television.
Update: Disney has settled the ESPN streaming fees class action lawsuit after three years of legal battles. The agreement follows allegations that Disney inflated live TV streaming prices through mandatory ESPN inclusion and anticompetitive contract terms. The confidential settlement impacts subscribers of YouTube TV, DirecTV Stream, and FuboTV.
What is the Disney Settles ESPN Streaming Fees Class Action Lawsuit?
The Disney Settles ESPN Streaming Fees Class Action Lawsuit refers to a legal case where subscribers of YouTube TV, DirecTV Stream, and FuboTV accused Disney of inflating live TV streaming prices. Plaintiffs claimed Disney forced platforms to include ESPN in base packages and used most-favored-nation clauses to keep prices high across the market.
The case began in 2022 and ended in June 2025 with a confidential settlement. While terms remain sealed, the agreement may involve subscriber compensation and could influence how streaming services bundle channels in the future.
What Is the Timeline of the Disney ESPN Streaming Lawsuit?
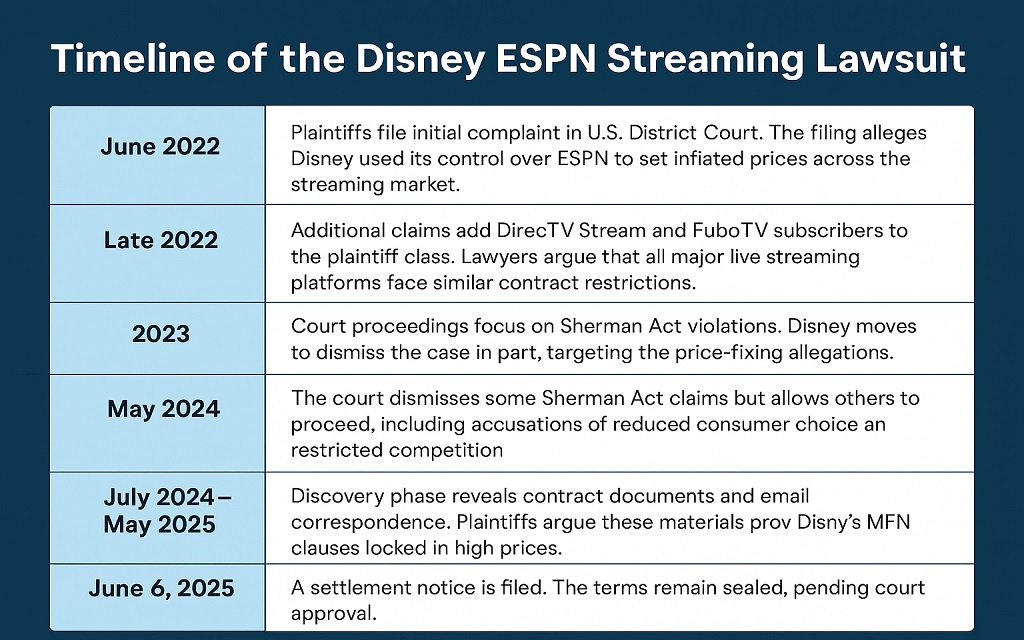
The case began in June 2022 when YouTube TV subscribers filed a federal lawsuit. They claimed Disney forced streaming platforms to carry ESPN in base packages, increasing subscription prices.
| Date / Period | Event Description |
|---|---|
| June 2022 | Plaintiffs file initial complaint in U.S. District Court, alleging Disney used its control over ESPN to set inflated prices across the streaming market. |
| Late 2022 | Additional claims add DirecTV Stream and FuboTV subscribers to the plaintiff class. Lawyers argue that all major live streaming platforms face similar contract restrictions. |
| 2023 | Court proceedings focus on Sherman Act violations. Disney moves to dismiss the case in part, targeting the price-fixing allegations. |
| May 2024 | The court dismisses some Sherman Act claims but allows others to proceed, including accusations of reduced consumer choice and restricted competition. |
| July 2024 – May 2025 | The discovery phase reveals contract documents and emails. Plaintiffs argue these prove Disney’s MFN clauses kept prices high. |
| June 6, 2025 | Settlement notice filed. Terms remain sealed, pending court approval. |
This sequence shows a typical class action trajectory, from initial filing to eventual confidential resolution.
What Were the Main Allegations Against Disney?
The lawsuit centered on two central claims: forced ESPN bundling and anticompetitive MFN clauses.
- Forced Bundling of ESPN
Plaintiffs argued Disney required streaming providers to include ESPN in their standard packages, preventing cheaper “sports-free” subscription options. Even non-sports fans paid for ESPN. - Most Favored Nation Clauses
Disney’s contracts allegedly contained MFN provisions, meaning any favorable term given to one distributor had to be extended to all others. This kept prices uniformly high across the market. - Price Inflation
The complaint claimed YouTube TV’s price rose from $35 to $65 per month after Disney imposed these terms. DirecTV Stream and FuboTV allegedly faced similar cost pressures. - Reduced Consumer Choice
Without the ability to offer packages without ESPN, streaming services could not differentiate pricing based on content preference.
How Did These Practices Allegedly Harm Consumers?
It is essential to understand the impact in both direct and indirect terms.
- Direct Financial Impact
Subscribers paid higher monthly fees, even if they had no interest in ESPN content. For a family subscribed for three years, this could mean several hundred dollars in added costs. - Market-Wide Pricing Pressure
Because MFN clauses forced all distributors to adopt similar rates, competition could not drive prices down. Smaller providers could not undercut larger ones. - Barrier to Entry for New Services
Start-up streaming companies faced entry costs that made competitive pricing impossible. This reduced innovation and variety in the streaming market.
An example from the case described a planned sports-free streaming platform that abandoned its launch due to unavoidable ESPN costs.
What Are the Settlement Details?
The settlement resolves all pending claims in the class action.
Parties Involved:
- Disney (parent company of ESPN)
- Plaintiffs representing subscribers of YouTube TV, DirecTV Stream, and FuboTV
Terms:
- Confidential, pending court approval
- Could involve monetary compensation and contract term changes
- Potential eligibility for affected subscribers
Relief Sought Before Settlement:
- Monetary damages for overpayments
- Injunctive relief to allow sports-free subscription tiers
- Contract revisions to remove MFN restrictions
While specific amounts are unknown, industry observers expect that if monetary relief is included, claim payouts could range from modest individual checks to larger sums for long-term subscribers.
Must Read: Nelnet Lawsuit: Complete Legal Guide for Borrowers
What Is the Legal and Procedural Context?
This case falls under federal antitrust law, specifically the Sherman Act.
Sherman Act Basics
- Section 1 prohibits contracts that unreasonably restrain trade.
- Section 2 targets monopolization and attempts to monopolize a market.
Disney’s Position
Disney denied wrongdoing, claiming ESPN’s value justified its inclusion in base packages and that MFN clauses ensured fair treatment among distributors.
Plaintiffs’ Position
Plaintiffs argued the practices restricted competition and harmed consumers by eliminating pricing flexibility.
Court Rulings
- Some claims were dismissed (e.g., pure price-fixing allegations without direct proof).
- Other claims survived, including reduced consumer choice and anticompetitive contract structuring.
Attorney Disputes
In July 2025, Reuters reported internal disagreements between law firms Bathaee Dunne LLP and DiCello Levitt over control of settlement talks.
How Does This Case Compare to Historical Antitrust Actions?
There have been similar bundling disputes in other industries.
- Cable TV Bundling Cases
In the 2010s, cable providers faced lawsuits for forcing subscribers to buy large channel bundles. Courts often weighed consumer harm against the business rationale for bundling. - Sports Rights Disputes
The NFL Sunday Ticket antitrust litigation targeted exclusive distribution arrangements that raised prices for football fans. - Tech Platform MFN Cases
Amazon faced antitrust scrutiny for MFN clauses in e-book sales, which critics said kept prices artificially high—the Disney ESPN case shares elements with each of these, combining content exclusivity with market dominance.
What Does This Mean for ESPN and Live Streaming?
The settlement could signal a shift in how sports networks distribute content. If Disney adjusts contracts:
- Platforms may offer sports-free plans
- MFN clauses could be weakened or removed
- Pricing flexibility could increase
ESPN remains a major driver of live TV subscriptions. According to S&P Global Market Intelligence, ESPN commands some of the highest carriage fees in the industry, estimated at over $9 per subscriber per month.
If those fees become optional for consumers, the entire streaming TV pricing model could change.
How Can Subscribers Check Eligibility for Compensation?
If you subscribed to one of the affected platforms between 2022 and 2025, you may qualify for settlement benefits.
Steps:
- Watch for official court-approved notices.
- Gather proof of subscription (billing statements, emails).
- File a claim before the deadline.
Settlement administrators typically create dedicated websites with claim forms, FAQs, and submission instructions.
Could This Lead to Industry-Wide Change?
Yes. Other streaming and cable disputes could follow this model, especially if consumer advocacy groups see success in challenging forced bundling.
Potential Industry Shifts:
- More à la carte channel options
- Lower entry barriers for new streaming platforms
- Increased antitrust enforcement in the media sector
Congress has held hearings on cable and streaming pricing before. A case like this could revive legislative interest in subscription transparency.
FAQs
Conclusion
The Disney ESPN streaming fees class action settlement ends a major fight over sports content pricing in the digital age. While the exact terms remain sealed, the case may pave the way for more flexible and affordable streaming options. Consumers should monitor announcements for claim instructions and consider how this legal outcome could reshape the streaming market.
Disclaimer: This article provides a general overview of the Disney Settles ESPN Streaming Fees Class Action lawsuit, based on publicly available information, and is intended for informational purposes only. It is not legal advice.
Musarat Bano is a content writer for JudicialOcean.com who covers lawsuits, legal news, and general legal topics. Her work focuses on research-based, informational content developed from publicly available sources and is intended to support public awareness. She does not provide legal advice or professional legal services.




